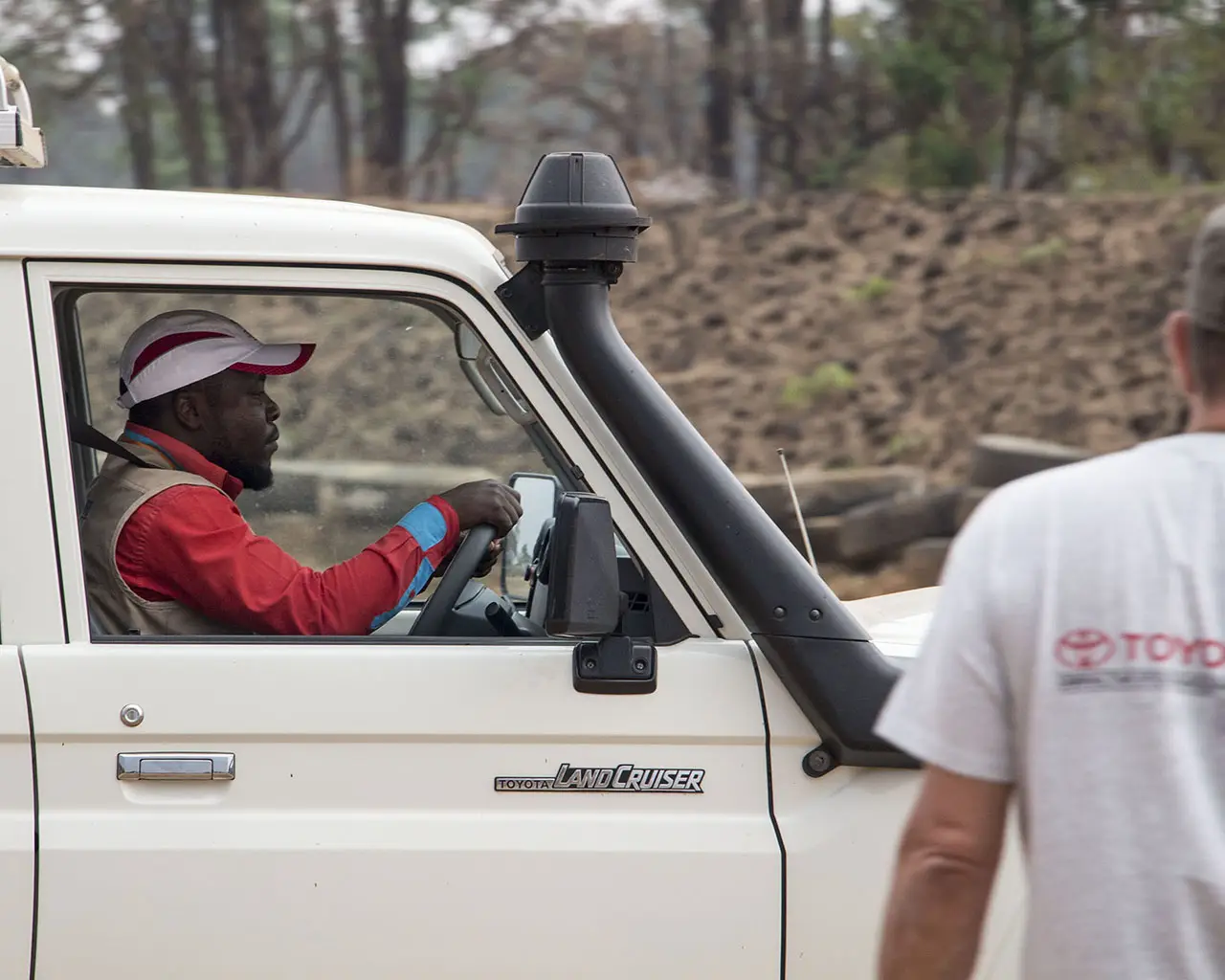
TGS is Toyota Tsusho Corporation's specialised distributor, appointed on behalf of Toyota Motor Corporation, for its direct sales scheme to the UN, International Humanitarian Aid and Conservation Organisations worldwide.


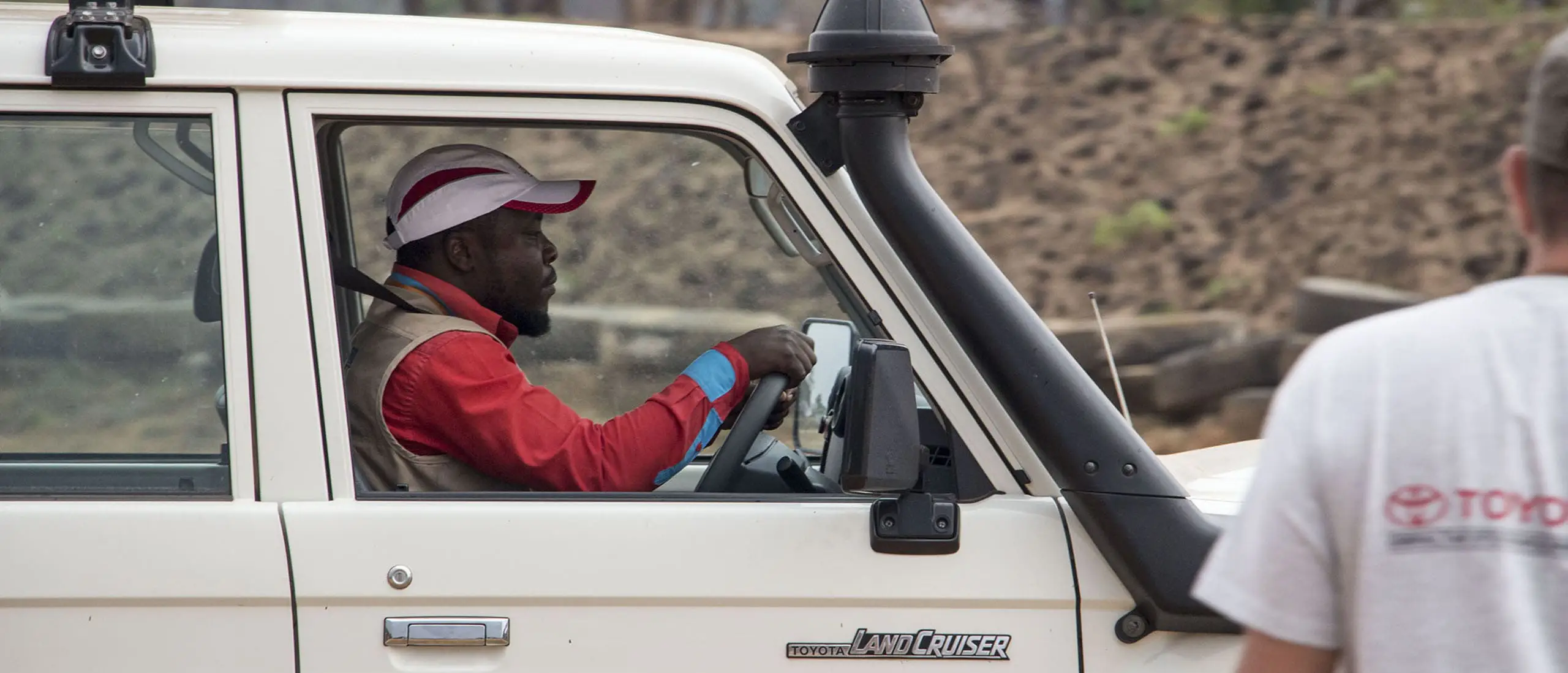
TGS headquarters are in Gibraltar, and there is an additional sales office in the USA. From its stocking locations in Gibraltar and Dubai, TGS distributes Toyota vehicles to customers worldwide.
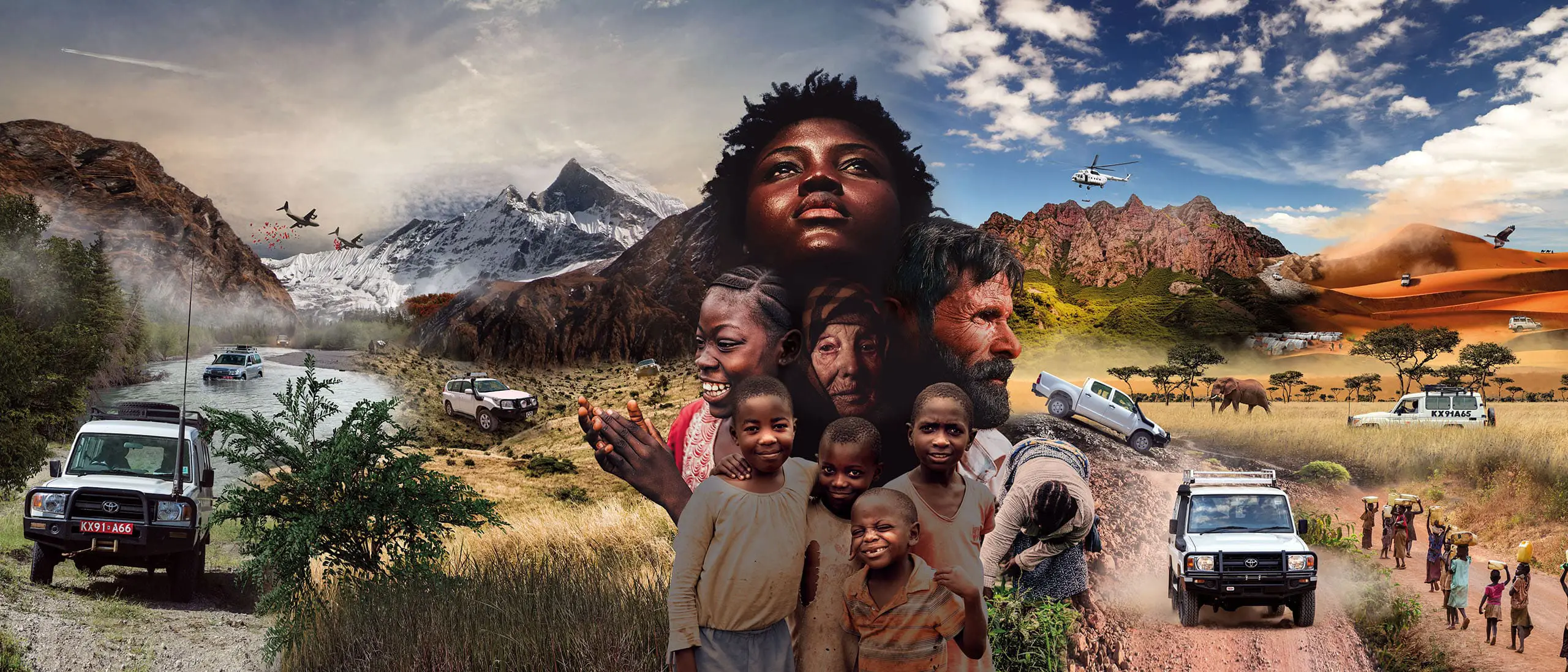


Marking 28 years of delivering mobility solutions through our people to the UN and aid organisations worldwide.


Are you prepared to make an impact? Explore our dynamic range of Toyota vehicles engineered to support your aid operations and tackle the world's harshest conditions. Our expert team will help you select the right Toyota for your operations.
Find Out More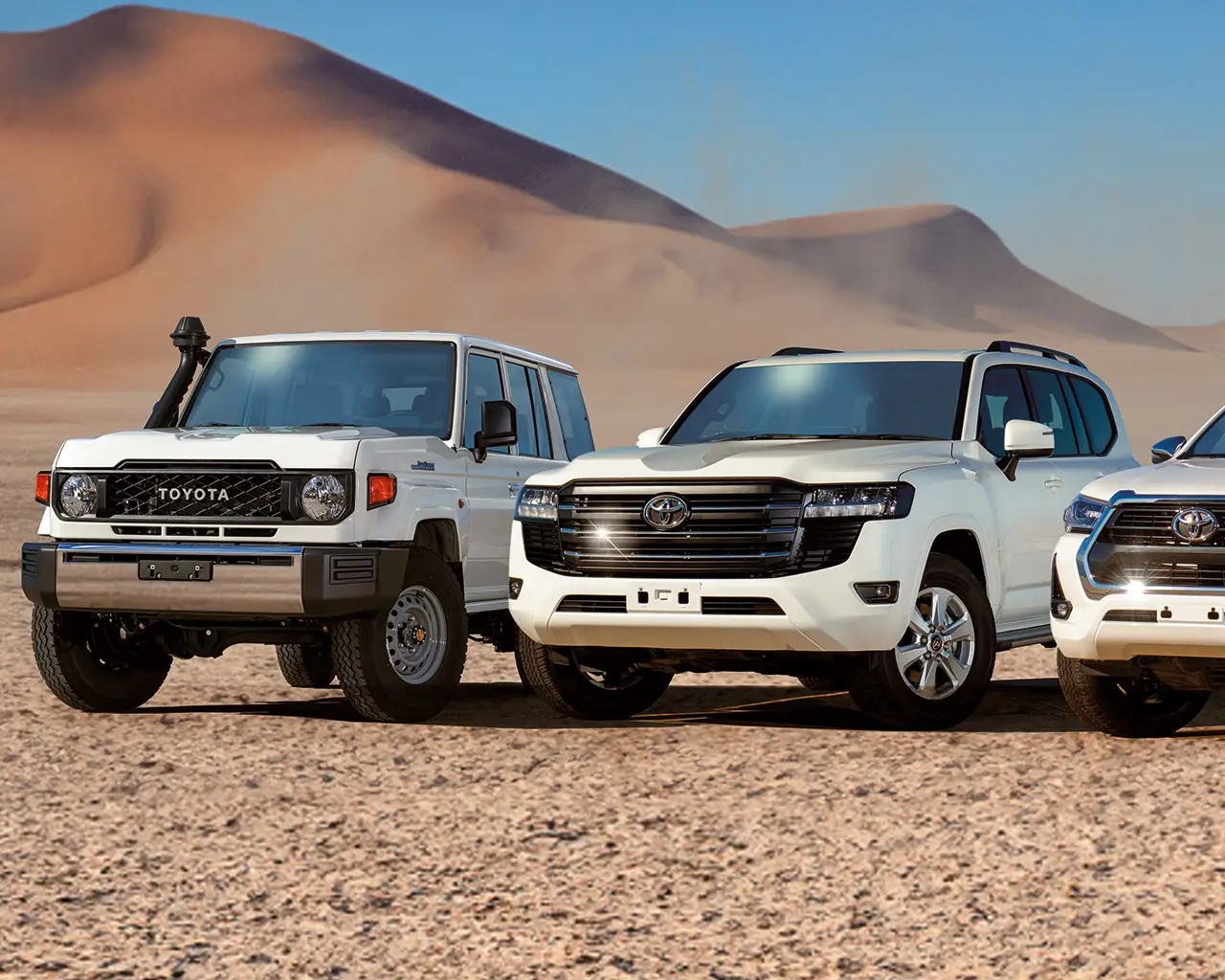
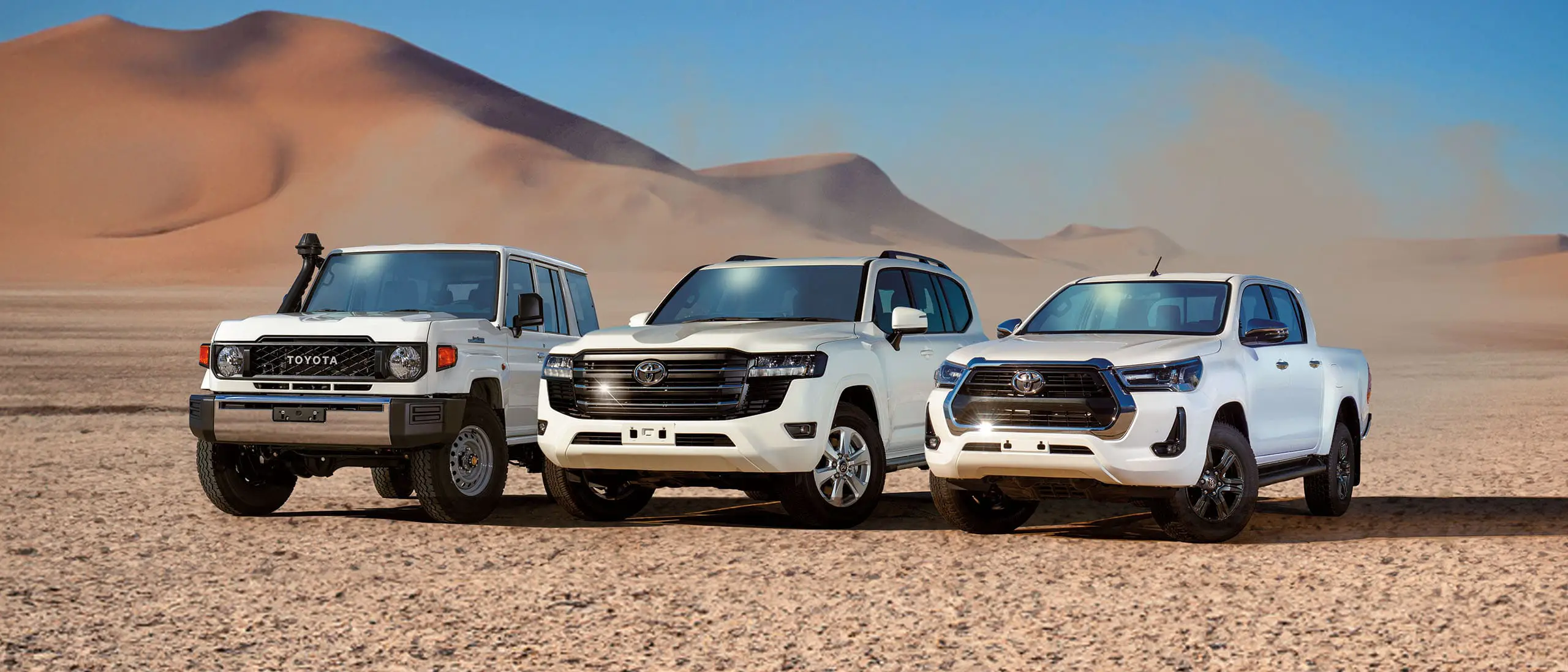

"Where the UN, NGOs, international aid agencies and governments come to buy their vehicles"

Enhance your Toyota with our extensive range of Options and Accessories. Ensuring that your Toyota is ready to face some of the harshest conditions in the world can make all the difference in delivering critical supplies to those in remote locations. Explore our extensive range of accessories to ensure you have the right tools to make that difference.
Find Out More

"TGS, it's automotive Amazon for international aid"

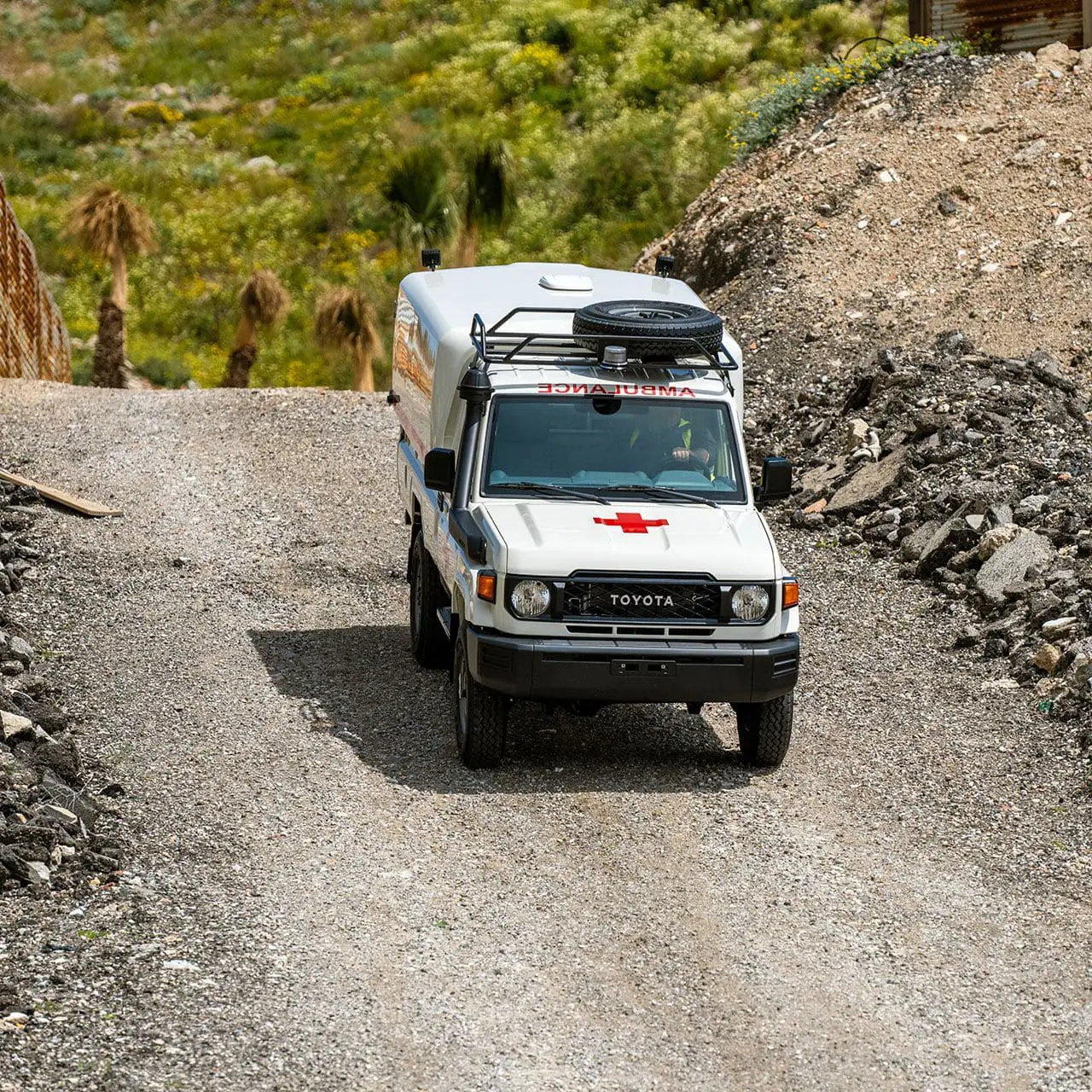
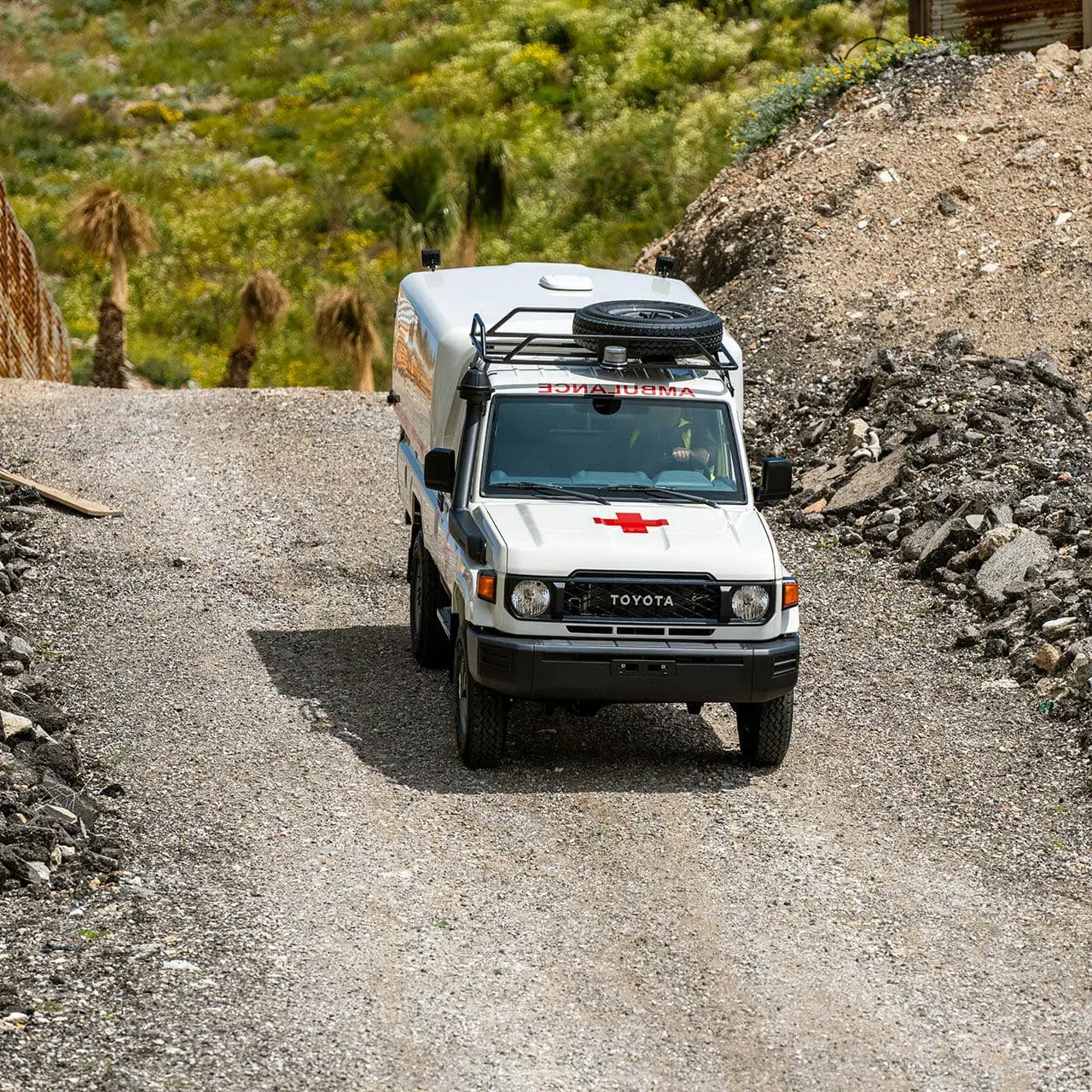
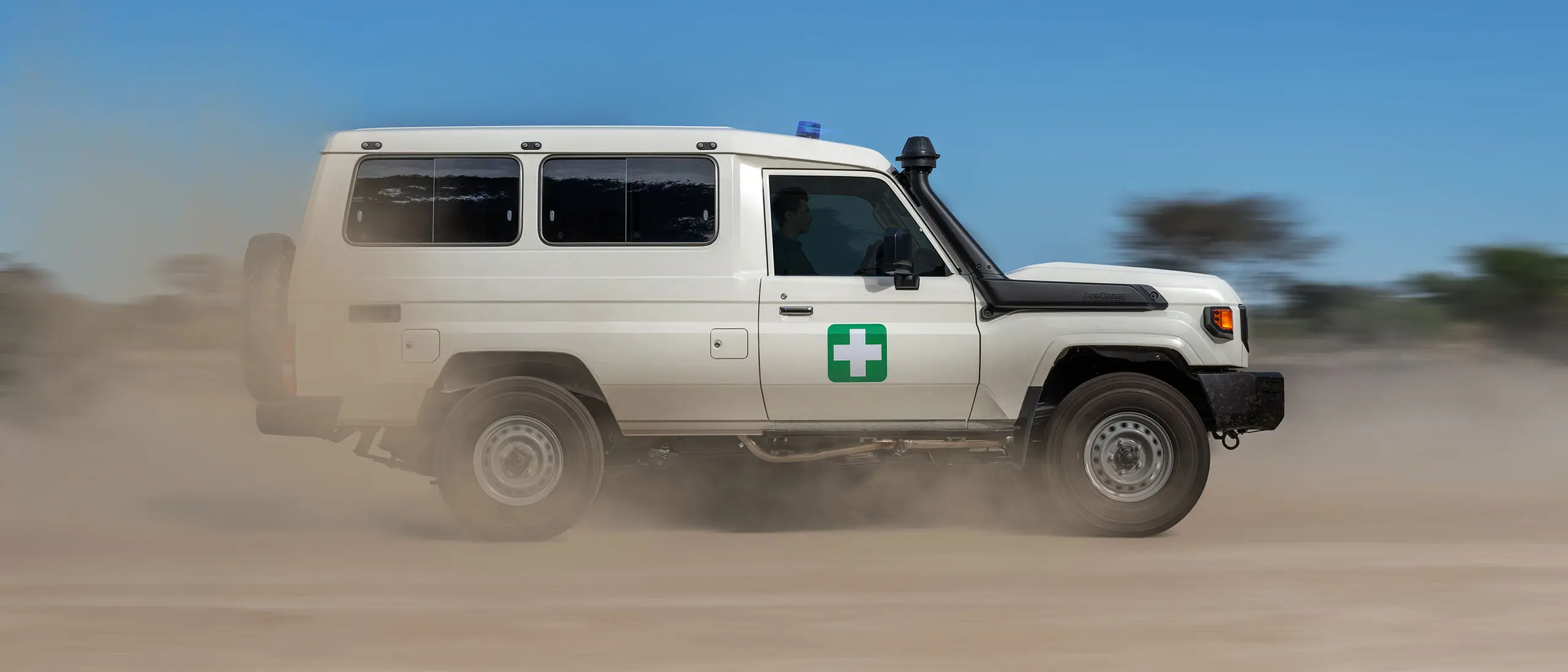
TGS ambulances provide a real lifeline to those needing urgent medical attention in rural communities. TGS offers a range of ambulance conversions based on our Land Cruiser 70 Series and our Hiace Commuter Bus.
Find Out More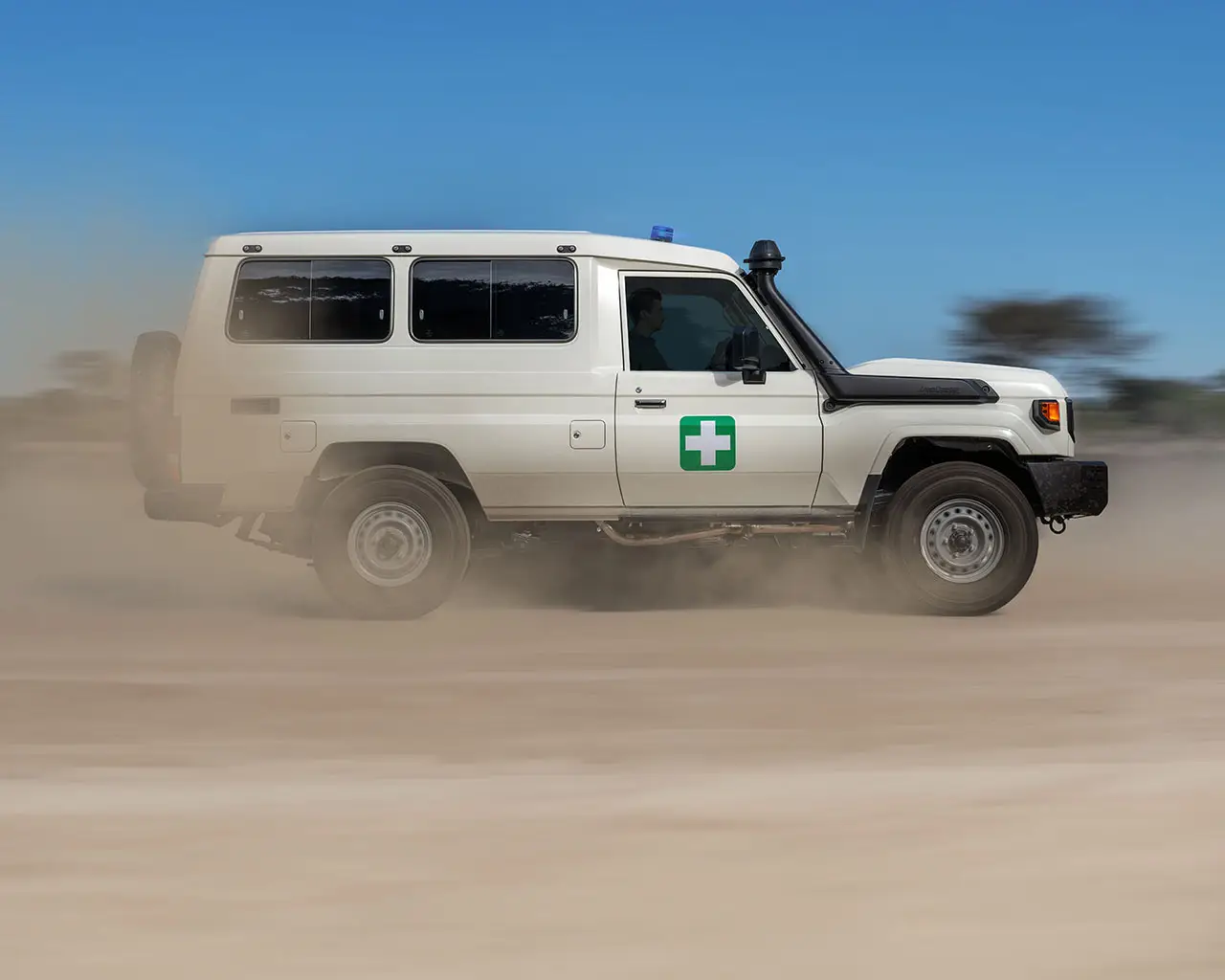

Humanitarian and conservation organisations strive to change lives. Whether delivering lifesaving supplies to people in remote locations or protecting endangered species, your organisation's work demands reliable, efficient, and operation-ready vehicles. TGS is an expert in customising our range of Toyota vehicles to meet your specific requirements.
Find Out More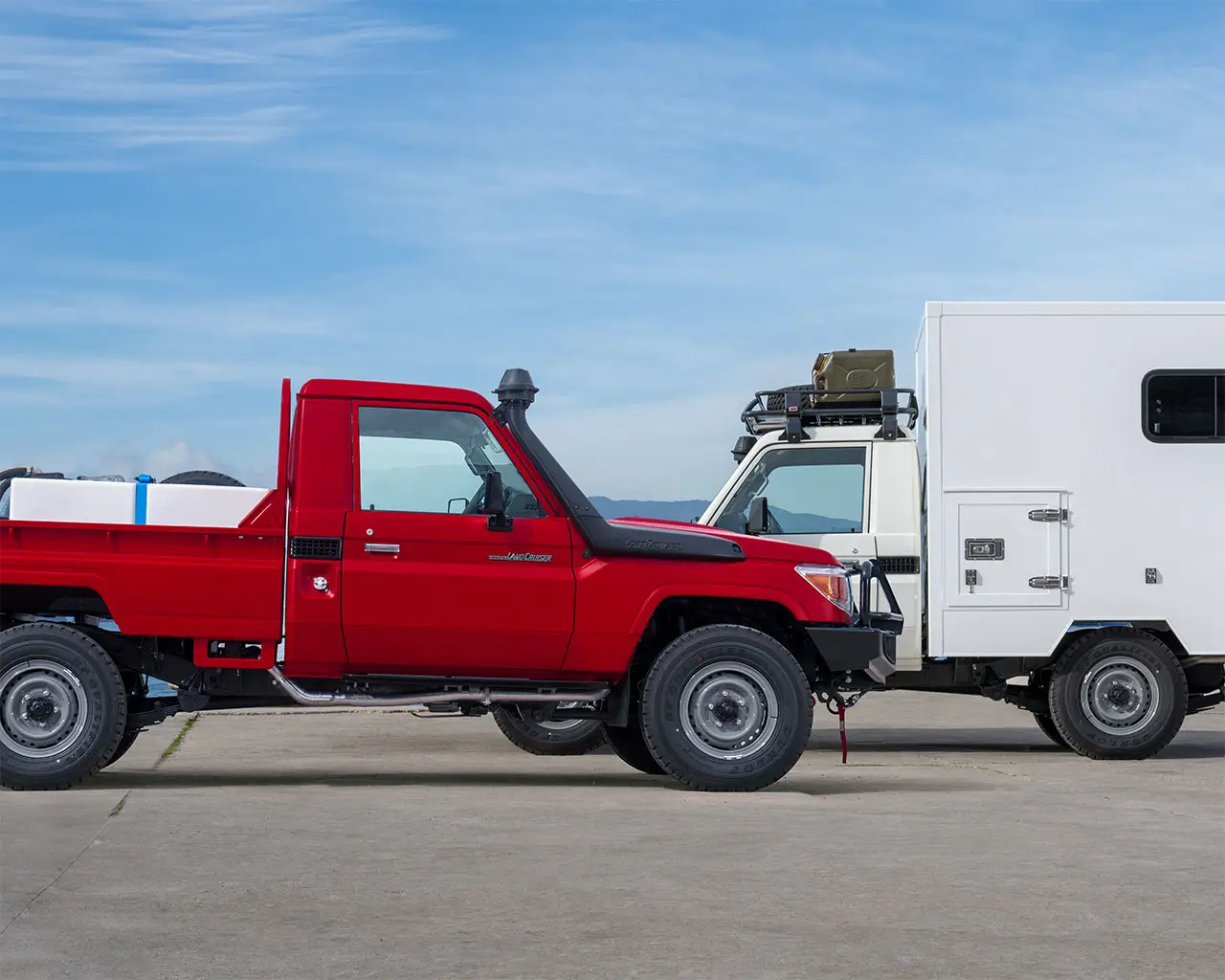
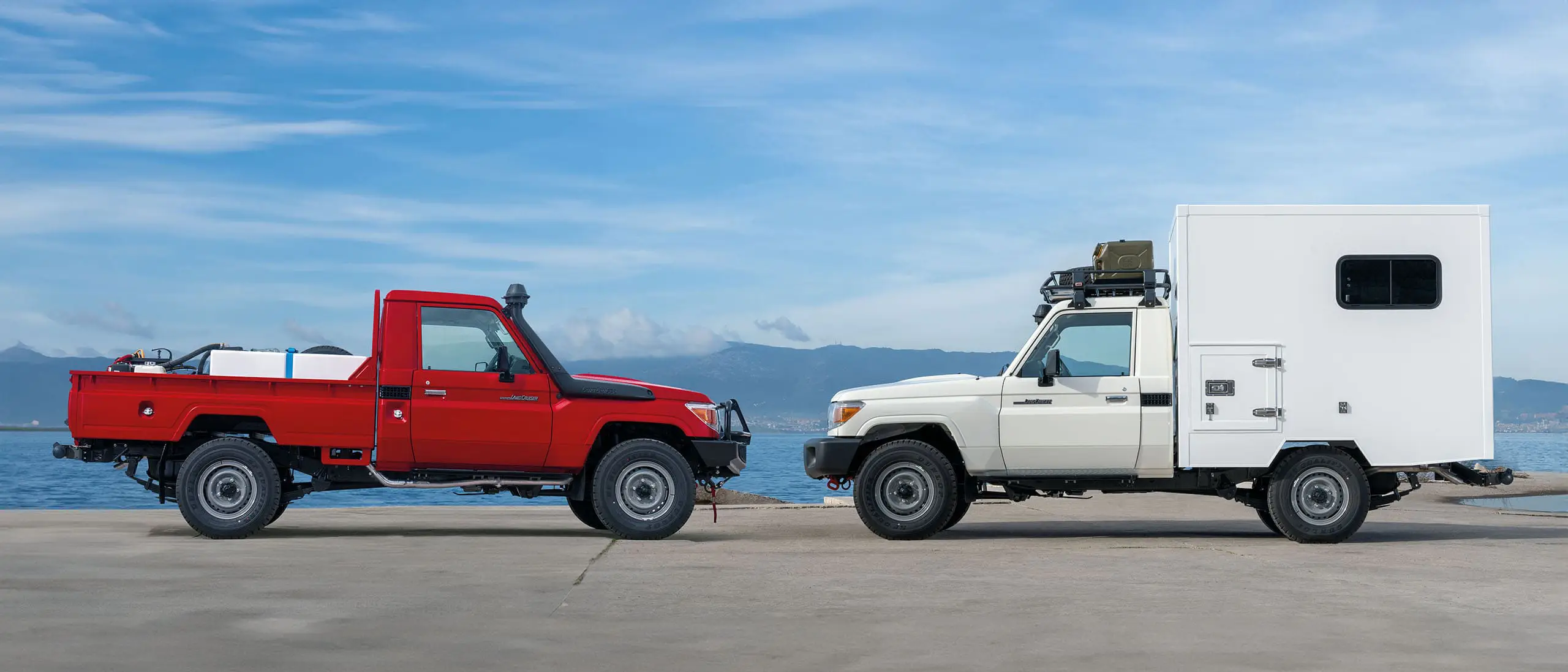

The TGS Fleet Services provides award-winning training and consultation services encompassing technical vehicle knowledge, road safety, fleet management, humanitarian and aid responsibilities, security, and educational training.
Find Out More
